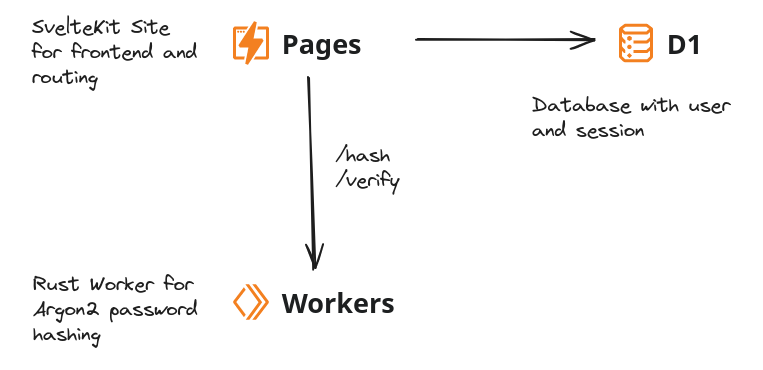
 Cloudflare resources used
Cloudflare resources used
Overview
This tutorial will provide an example of how to use Lucia Auth in Cloudflare with an Argon2 Rust Worker. By using a Rust Cloudflare Worker, it is possible to hash with minimal performance downsides when compared to pure JavaScript implementations. This means no compromises in the hashing algorithm, no need to use weaker algorithms (ex. PBKDF2) to avoid exceeding the CPU limit.
To use Lucia Auth on Cloudflare, we also need a database. This tutorial will also show you how to use Cloudflare D1 with Lucia Auth using DrizzleORM.
Example of complete project:
This tutorial assumes some basic familiarity with the following libraries and frameworks:
- SvelteKit: JavaScript web framework used as frontend and router for this tutorial.
- DrizzleORM: TypeScript ORM used for creating queries and schema. Used with Lucia Auth and Cloudflare D1 for user and session database.
- Lucia Auth: Typescript authentication library. Provides easy to use abstractions for handling users and sessions. Supports use with SvelteKit and DrizzleORM
- Cloudflare Pages: Supports deployment of full stack frameworks such as SvelteKit.
- Cloudflare Rust Workers: Allows creating Cloudflare Workers with Rust. Workers can then be called using Service Bindings.
- Cloudflare D1: Cloudflare serverless database built on
sqlite
Make sure you have the following installed and setup:
- NodeJS
- Cloudflare Account
- Cloudflare Paid Workers Plan.
- The free tier plan might work but hashing will use ~ 100 ms of CPU time, exceeding the 10 ms CPU time limit for free plans.
- https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/platform/limits/
- Wrangler with connection to your Cloudflare Account
- Rust with
wasm32-unknown-unknowntool chain
Debugging Common Issues:
- Cloudflare features change quickly, please check the docs.
- Make sure your
wranglerversion is up to date, this tutorial is uses"wrangler": "^3.48.0" - Check the error logs in Cloudflare. If you are receiving a CPU limit error, it may be related to the 10 ms CPU time limit for free plans.
- DrizzleKit currently has issues with D1. Use
wranglerfor migrations. - When developing in local dev, make sure that the worker dev server is running before the SvelteKit dev server.
Links
- https://github.com/magicalpuffin/tutorial-cloudflare-lucia-argon2
- https://github.com/glotlabs/argon2-cloudflare
Create a Rust Cloudflare Worker
Cloudflare uses V8, which prevents us from using any Argon2 implementations with Node bindings. This includes the Rust Argon2 binding provided by @node-rs/argon2 which is recommended by Lucia (through oslo) for password hashing.
A pure JavaScript implementation would be too slow and Cloudflare Web Crypto doesn’t have any good password hashing algorithms. Solution? We create a Rust Cloudflare Worker and use a Rust implementation of Argon2. Then we use a Cloudflare Service Binding to call the Worker whenever we need password hashing.
Fortunately, someone has already implemented this! All we have to do is just connect everything together. Full credit to its author, Petter Rasmussen:
Note: I would recommend reading through the source code and extending the implementation to meet your own needs. The Rust crate used for argon2 is from https://github.com/RustCrypto/password-hashes
Lets first create and test the Rust Worker. Make sure you already have Rust setup.
Clone the repository using:
git clone https://github.com/glotlabs/argon2-cloudflareChange directory to the folder and install the latest version of wrangler
cd argon2-cloudflare/
npm i -D wrangler@latestIf needed, update the wrangler.toml. In this tutorial, I renamed the worker to tutorial-argon2 and disabled the dev route to ensure we are always using the service binding.
name = "tutorial-argon2"
main = "build/worker/shim.mjs"
compatibility_date = "2023-03-22"
workers_dev = false
# ...Run the worker in dev. This builds the Rust worker and makes it accessible at http://localhost:8787
npm run dev Rust worker running in dev after building
Rust worker running in dev after building
Test the worker using curl:
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8787/hash -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"password": "helloworld"}'Deploy the worker:
npm run deployCreate the SvelteKit Site
For this tutorial, I will be creating a SvelteKit site, however, this should work with whatever framework you are using as long as it is supported by Cloudflare and Lucia.
Create the SvelteKit site following the Cloudflare SvelteKit Framework Guide. In this example, I named the site tutorial-sveltekit and will be using Typescript.
npm create cloudflare@latest tutorial-sveltekit -- --framework=svelteChange directories to tutorial-sveltekit and install libraries:
- If installed using the
npm create cloudflarecommand,wranglershould already be installed and up to date. - It is optional to install
better-sqlite3. This is used for accessing the localsqlitedatabase and is unrelated to Cloudflare D1.
cd tutorial-sveltekit/
npm i -D wrangler@latest
npm i -D lucia @lucia-auth/adapter-sqlite
npm i -D drizzle-orm drizzle-kit better-sqlite3Note: The rest of these steps will be from the tutorial-sveltekit directory unless otherwise specified.
Create Cloudflare D1 Database
Create the Cloudflare D1 database. For this tutorial, I named the database tutorial-d1-argon2. After you run the command, it will list out a database_id, make sure you add this to your wrangler.toml.
npx wrangler d1 create tutorial-d1-argon2Update wrangler.toml to include your database and the Rust worker as a service binding.
pages_build_output_dirwill make Cloudflare use yourwrangler.tomlfor the production deployment configuration.- Add a
migrations_dirto enable use ofwrangler d1 migrations - The resources are listed in
env.productionwill be configured in the production deployment - You can run
npm run deploynow to check if resources are assigned in the production deployment.
name = "tutorial-sveltekit"
compatibility_date = "2024-04-05"
pages_build_output_dir = ".svelte-kit/cloudflare"
[[services]]
binding = "ARGON2"
service = "tutorial-argon2"
[[d1_databases]]
binding = "DB"
database_name = "tutorial-d1-argon2"
database_id = ""
migrations_dir = "drizzle"
[env.production]
compatibility_date = "2024-04-05"
[[env.production.services]]
binding = "ARGON2"
service = "tutorial-argon2"
environment = "production"
[[env.production.d1_databases]]
binding = "DB"
database_name = "tutorial-d1-argon2"
database_id = ""Setup DrizzleORM
Setup DrizzleORM following the docs
// src/lib/db/db.ts
import { drizzle } from 'drizzle-orm/d1';
import * as schema from '$lib/db/schema';
export function initializeDrizzle(D1: D1Database) {
return drizzle(D1, { schema });
}Create the schema following Lucia Auth docs on DrizzleORM for sqlite
// src/lib/db/schema.ts
import { sqliteTable, text, integer } from 'drizzle-orm/sqlite-core';
export const userTable = sqliteTable('user', {
id: text('id').primaryKey(),
username: text('username').unique(),
hashedPassword: text('hashed_password')
});
export const sessionTable = sqliteTable('session', {
id: text('id').primaryKey(),
userId: text('user_id')
.notNull()
.references(() => userTable.id),
expiresAt: integer('expires_at').notNull()
});Create a drizzle.config.ts file.
- This will use
better-sqliteto access the local.sqlitedatabase generated by miniflare in.wrangler/state/v3/d1after migrations are run. - This config will only work on the local database. See links for GitHub issues of DrizzleKit Cloudflare D1 connection issues.
// drizzle.config.ts
import type { Config } from "drizzle-kit";
export default {
schema: "./src/lib/db/schema.ts",
out: "./drizzle",
driver: "better-sqlite",
dbCredentials: {
url: process.env.LOCAL_DB!,
},
} satisfies Config;Create the migrations:
npx drizzle-kit generate:sqliteUse wrangler to run the migrations
- By default the migrations apply only to the local database. You can run the migrations on the production database by adding a
--remoteflag - After running the migrations, a
.sqlitedatabase should appear in.wrangler/state/v3/d1 - https://developers.cloudflare.com/d1/reference/migrations/`
npx wrangler d1 migrations list tutorial-d1-argon2
npx wrangler d1 migrations apply tutorial-d1-argon2Create a .env file and add the local .sqlite database generated by miniflare
- This allows us to use DrizzleKit studio on the local database
LOCAL_DB = ".wrangler/state/v3/d1/..."DrizzleKit Studio should be working
npx drizzle-kit studioSetup Lucia Auth
Setup Lucia Auth based on docs
- https://lucia-auth.com/getting-started/sveltekit
- https://lucia-auth.com/tutorials/username-and-password/sveltekit
Because of Cloudflare D1, Lucia will need to be initialized from a function.
// src/lib/server/auth.ts
import { Lucia } from "lucia";
import { D1Adapter } from "@lucia-auth/adapter-sqlite";
import { dev } from "$app/environment";
export function initializeLucia(D1: D1Database) {
const adapter = new D1Adapter(D1, {
user: "user",
session: "session",
});
return new Lucia(adapter, {
sessionCookie: {
attributes: {
// set to `true` when using HTTPS
secure: !dev,
},
},
getUserAttributes: (attributes) => {
return {
username: attributes.username,
};
},
});
}
declare module "lucia" {
interface Register {
Lucia: ReturnType<typeof initializeLucia>;
DatabaseUserAttributes: DatabaseUserAttributes;
}
}
interface DatabaseUserAttributes {
username: string;
}
During each request, Lucia will need to be initialized using the database from environment.
// src/hooks.server.ts
import { initializeLucia } from '$lib/server/auth';
import type { Handle } from '@sveltejs/kit';
export const handle: Handle = async ({ event, resolve }) => {
const lucia = initializeLucia(event.platform!.env.DB);
const sessionId = event.cookies.get(lucia.sessionCookieName);
if (!sessionId) {
event.locals.user = null;
event.locals.session = null;
return resolve(event);
}
const { session, user } = await lucia.validateSession(sessionId);
if (session && session.fresh) {
const sessionCookie = lucia.createSessionCookie(session.id);
// sveltekit types deviates from the de-facto standard
// you can use 'as any' too
event.cookies.set(sessionCookie.name, sessionCookie.value, {
path: '.',
...sessionCookie.attributes
});
}
if (!session) {
const sessionCookie = lucia.createBlankSessionCookie();
event.cookies.set(sessionCookie.name, sessionCookie.value, {
path: '.',
...sessionCookie.attributes
});
}
event.locals.user = user;
event.locals.session = session;
return resolve(event);
};In addition to Lucia, add the database and service binding to app.d.ts. This should resolve type errors when accessing DB or ARGON2 in event.platform!.env.
declare global {
namespace App {
interface Locals {
user: import('lucia').User | null;
session: import('lucia').Session | null;
}
interface Platform {
env: {
DB: D1Database;
ARGON2: Fetcher;
};
context: {
// eslint-disable-next-line @typescript-eslint/no-explicit-any
waitUntil(promise: Promise<any>): void;
};
caches: CacheStorage & { default: Cache };
}
}
}
export {};Create a custom CloudflareArgon2 class
- This constructor is a drop in replacement for the
Argon2idfromoslo/password - The
serviceBindingshould be theARGON2service binding fetchdoesn’t actually fetch at that URL, instead it communicates internally through the Cloudflare service binding.
// src/lib/server/argon2.ts
export class CloudflareArgon2 {
private serviceBinding: Fetcher;
private memorySize: number;
private iterations: number;
private parallelism: number;
constructor(
serviceBinding: Fetcher,
options?: {
memorySize?: number;
iterations?: number;
tagLength?: number;
parallelism?: number;
}
) {
this.serviceBinding = serviceBinding;
this.memorySize = options?.memorySize ?? 19456;
this.iterations = options?.iterations ?? 2;
this.parallelism = options?.parallelism ?? 1;
}
public async hash(password: string) {
const resp = await this.serviceBinding.fetch("http://internal/hash", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify({
password: password,
options: {
timeCost: this.iterations,
memoryCost: this.memorySize,
parallelism: this.parallelism,
},
}),
});
const { hash }: { hash: string } = await resp.json();
return hash;
}
public async verify(hash: string, password: string) {
const resp = await this.serviceBinding.fetch("http://internal/verify", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify({ password: password, hash: hash }),
});
const { matches }: { matches: boolean } = await resp.json();
return matches;
}
}Create Signup Page
<!-- src/routes/signup/+page.svelte -->
<script lang="ts">
import { enhance } from '$app/forms';
</script>
<h1>Sign up</h1>
<form method="post" use:enhance>
<label for="username">Username</label>
<input name="username" id="username" /><br />
<label for="password">Password</label>
<input type="password" name="password" id="password" /><br />
<button>Continue</button>
</form>// src/routes/signup/+page.server.ts
import { initializeLucia } from "$lib/server/auth";
import { fail, redirect } from "@sveltejs/kit";
import { generateId } from "lucia";
import { userTable } from "$lib/db/schema";
import { initializeDrizzle } from "$lib/db/db";
import { CloudflareArgon2 } from "$lib/server/argon2";
import type { Actions } from "./$types";
import { eq } from "drizzle-orm";
export const actions: Actions = {
default: async (event) => {
const lucia = initializeLucia(event.platform!.env.DB);
const db = initializeDrizzle(event.platform!.env.DB);
const formData = await event.request.formData();
const username = formData.get("username");
const password = formData.get("password");
// username must be between 4 ~ 31 characters, and only consists of lowercase letters, 0-9, -, and _
// keep in mind some database (e.g. mysql) are case insensitive
if (
typeof username !== "string" ||
username.length < 3 ||
username.length > 31 ||
!/^[a-z0-9_-]+$/.test(username)
) {
return fail(400, {
message: "Invalid username",
});
}
if (
typeof password !== "string" ||
password.length < 6 ||
password.length > 255
) {
return fail(400, {
message: "Invalid password",
});
}
const userId = generateId(15);
const hashedPassword = await new CloudflareArgon2(
event.platform!.env.ARGON2
).hash(password);
// Check if username is already used
const existingUser = await db.query.userTable.findFirst({
where: eq(userTable.username, username),
});
if (existingUser) {
return fail(400, {
message: "Username already taken",
});
}
// maybe return user?
await db.insert(userTable).values({ id: userId, username, hashedPassword });
const session = await lucia.createSession(userId, {});
const sessionCookie = lucia.createSessionCookie(session.id);
event.cookies.set(sessionCookie.name, sessionCookie.value, {
path: ".",
...sessionCookie.attributes,
});
redirect(302, "/");
},
};Create Login Page
<!-- src/routes/login/+page.svelte -->
<script lang="ts">
import { enhance } from '$app/forms';
</script>
<h1>Sign in</h1>
<form method="post" use:enhance>
<label for="username">Username</label>
<input name="username" id="username" /><br />
<label for="password">Password</label>
<input type="password" name="password" id="password" /><br />
<button>Continue</button>
</form>
// src/routes/login/+page.server.ts
import { initializeLucia } from "$lib/server/auth";
import { fail, redirect } from "@sveltejs/kit";
import { initializeDrizzle } from "$lib/db/db";
import { userTable } from "$lib/db/schema";
import { eq } from "drizzle-orm";
import { CloudflareArgon2 } from "$lib/server/argon2";
import type { Actions } from "./$types";
export const actions: Actions = {
default: async (event) => {
const lucia = initializeLucia(event.platform!.env.DB);
const db = initializeDrizzle(event.platform!.env.DB);
const formData = await event.request.formData();
const username = formData.get("username");
const password = formData.get("password");
if (
typeof username !== "string" ||
username.length < 3 ||
username.length > 31 ||
!/^[a-z0-9_-]+$/.test(username)
) {
return fail(400, {
message: "Invalid username",
});
}
if (
typeof password !== "string" ||
password.length < 6 ||
password.length > 255
) {
return fail(400, {
message: "Invalid password",
});
}
const existingUser = await db.query.userTable.findFirst({
where: eq(userTable.username, username.toLocaleLowerCase()),
});
if (!existingUser) {
return fail(400, {
message: "Incorrect username or password",
});
}
const validPassword = await new CloudflareArgon2(
event.platform!.env.ARGON2
).verify(existingUser.hashedPassword ?? "", password);
if (!validPassword) {
return fail(400, {
message: "Incorrect username or password",
});
}
const session = await lucia.createSession(existingUser.id, {});
const sessionCookie = lucia.createSessionCookie(session.id);
event.cookies.set(sessionCookie.name, sessionCookie.value, {
path: ".",
...sessionCookie.attributes,
});
redirect(302, "/");
},
};Create Home Page
<!-- routes/+page.svelte -->
<script lang="ts">
import { enhance } from "$app/forms";
import type { PageData } from "./$types.js";
export let data: PageData;
</script>
<p>Logged in as {data.username}</p>
<form method="post" use:enhance>
<button>Sign out</button>
</form>
// src/routes/+page.server.ts
import { redirect, fail } from '@sveltejs/kit';
import { initializeLucia } from '$lib/server/auth';
import type { PageServerLoad, Actions } from './$types';
export const load: PageServerLoad = async (event) => {
if (!event.locals.user) redirect(302, '/login');
return {
username: event.locals.user.username,
};
};
export const actions: Actions = {
default: async (event) => {
const lucia = initializeLucia(event.platform!.env.DB);
if (!event.locals.session) {
return fail(401);
}
await lucia.invalidateSession(event.locals.session.id);
const sessionCookie = lucia.createBlankSessionCookie();
event.cookies.set(sessionCookie.name, sessionCookie.value, {
path: '.',
...sessionCookie.attributes
});
redirect(302, '/login');
}
};Test Locally
Open a terminal in the Argon2 Cloudflare Worker directory and run dev
cd argon2-cloudflare/
npm run devOpen a terminal in SvelteKit site directory and run dev. The service binding on the SvelteKit site only works if the worker dev server is already running.
cd tutorial-sveltekit/
npm run devIf setup, start DrizzleKit Studio
cd tutorial-sveltekit/
npx drizzle-kit studio Sign up page
Sign up page
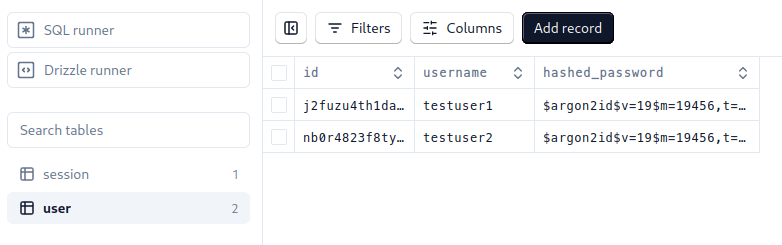 DrizzleKit Studio with local data
DrizzleKit Studio with local data
Deploy to Cloudflare
Run migrations on production database
npx wrangler d1 migrations list tutorial-d1-argon2 --remote
npx wrangler d1 migrations apply tutorial-d1-argon2 --remoteDeploy Argon2 Cloudflare Worker
cd argon2-cloudflare/
npm run deployDeploy SvelteKit site
cd tutorial-sveltekit/
npm run deploy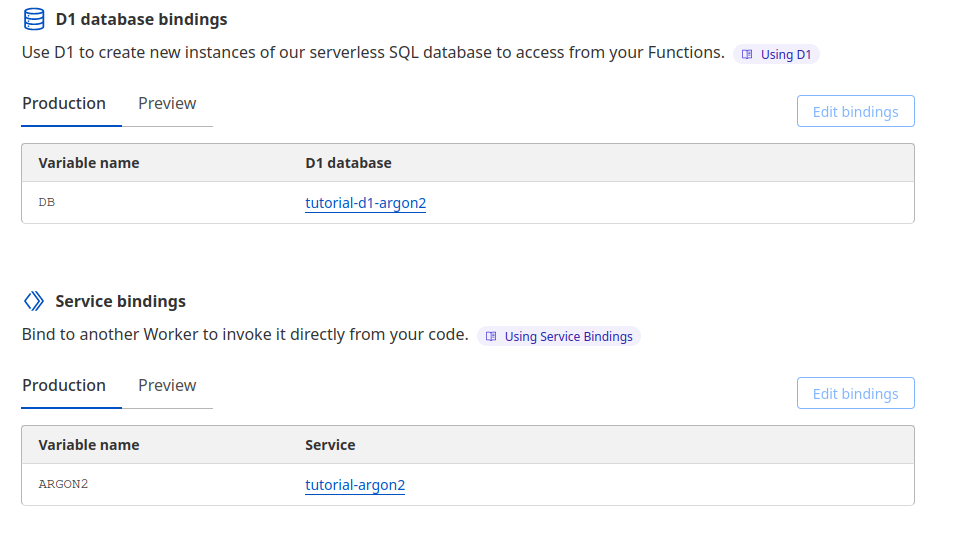 Bindings automatically setup in Cloudflare from wrangler.toml
Bindings automatically setup in Cloudflare from wrangler.toml
After deployment, you can check how long it takes to login. 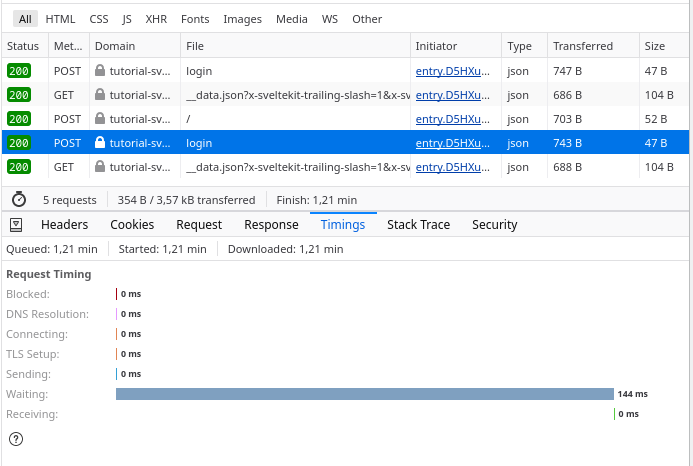 Response timing in Firefox for a login
Response timing in Firefox for a login
In Cloudflare, you can check how much CPU time is consumed when hashing. ~ 100 ms CPU time is high compared to normal workers, however, this is much better than pure JavaScript implementations (~ 2,000 ms CPU time for Lucia Scrypt and ~ 14,000 ms of CPU time for noble hashes Argon2id). 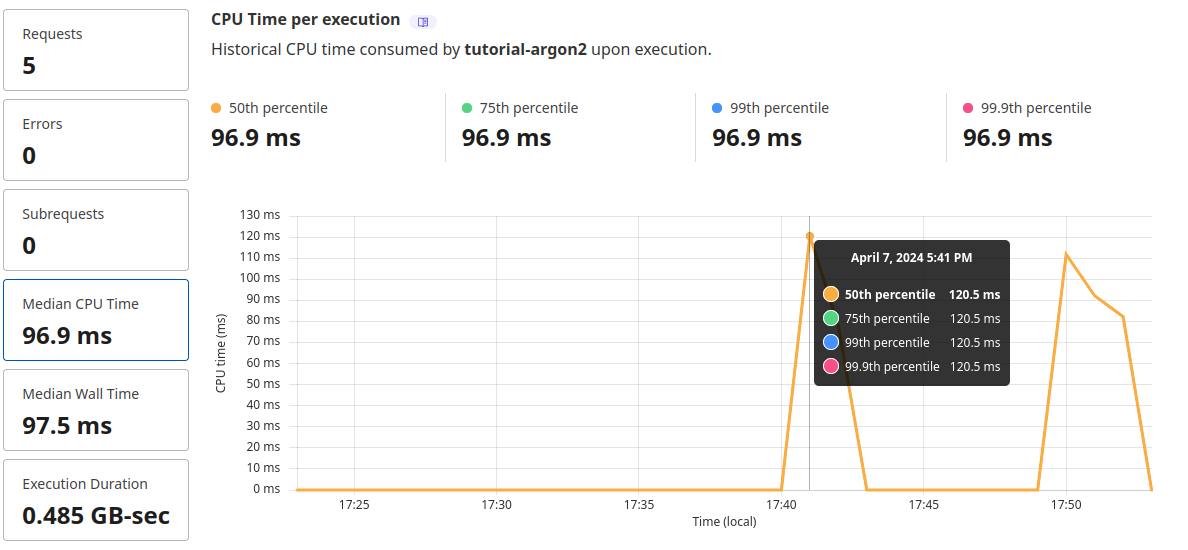 CPU time when running argon2
CPU time when running argon2
Bonus: A Pure JavaScript Implementation of Argon2 Example
- I don’t think a pure JavaScript implementation of Argon2 is ever practical because of how long it takes. But if you still need a pure JavaScript implementation of Argon2, try
@noble/hashes - If you try to run this in Cloudflare, you will likely receive a
Worker exceeded CPU time limiterror.
import { argon2id } from "@noble/hashes/argon2";
import { randomBytes } from "@noble/hashes/utils";
class NobleArgon2id {
private memorySize: number;
private iterations: number;
private parallelism: number;
constructor(options?: {
memorySize?: number;
iterations?: number;
tagLength?: number;
parallelism?: number;
}) {
this.memorySize = options?.memorySize ?? 19456;
this.iterations = options?.iterations ?? 2;
this.parallelism = options?.parallelism ?? 1;
}
public hash(password: string, salt?: Uint8Array) {
const saltUint8 = salt ?? randomBytes(8);
const hash = argon2id(password, saltUint8, {
t: this.iterations,
m: this.memorySize,
p: this.parallelism,
});
// remove padding to match other implementations
const saltBase64 = btoa(String.fromCharCode(...saltUint8)).replace(
/=+$/,
""
);
const hashBase64 = btoa(String.fromCharCode(...hash)).replace(/=+$/, "");
return `$argon2id$v=19$m=${this.memorySize},t=${this.iterations},p=${this.parallelism}$${saltBase64}$${hashBase64}`;
}
public verify(hash: string, password: string) {
const saltBase64 = hash.split("$")[4];
const saltUint8 = Uint8Array.from(atob(saltBase64), (char) =>
char.charCodeAt(0)
);
return this.hash(password, saltUint8) == hash;
}
}